Unexpected spark: Dwarf galaxies lit the early universe
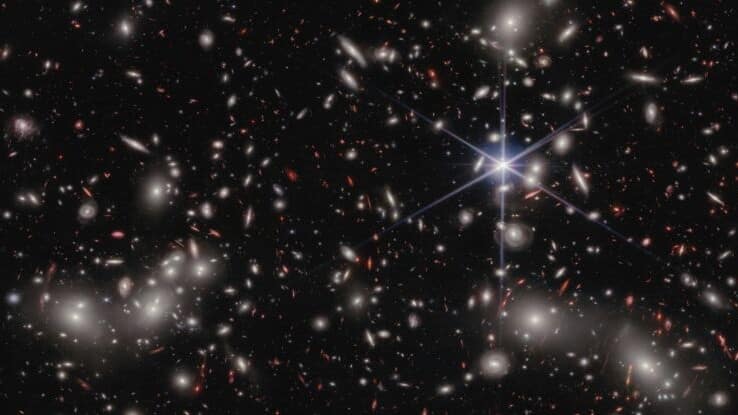
Scientists have uncovered the source of light in the early universe, attributing it to small dwarf galaxies. Data from the Hubble and James Webb Space Telescope revealed these galaxies flared into existence, clearing a foggy expanse of hydrogen in intergalactic space. Astrophysicist Iryna Chemerynska from the Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris emphasized this discovery's significance, stating, "This discovery unveils the crucial role played by ultra-faint galaxies in the early Universe's evolution."
Dwarf galaxies: The cosmic powerhouses
In early universe, dwarf galaxies were not only the most abundant but also far brighter than anticipated. A team led by astrophysicist Hakim Atek used data from a galaxy cluster called Abell 2744 to make this discovery. Atek noted, "These cosmic powerhouses collectively emit more than enough energy to get the job done." The research shows that dwarf galaxies outnumber large ones by 100 to 1, and their collective output is four times the ionizing radiation assumed for larger galaxies.
Further research needed to confirm findings
Despite the significant findings, more research is required to confirm the role of dwarf galaxies in the early universe's illumination. The team plans to study even more cosmic lens regions for a broader sample of early galactic populations. Astrophysicist Themiya Nanayakkara from Swinburne University of Technology in Australia commented on this development, saying, "We have now entered uncharted territory with the JWST." The research was published in Nature.
Understanding the universe's early evolution
The universe got filled with a hot, dense fog of ionized plasma within minutes of the Big Bang. As it cooled after roughly 300,000 years, protons and electrons began to form neutral hydrogen and a certain bit of helium gas. From this helium and hydrogen, the first stars were born. These stars emitted radiation strong enough to reionize the gas, allowing light to shine out by about one billion years post the Big Bang.
Dwarf galaxies challenge previous beliefs
Previously, scientists believed that powerful sources such as large galaxies undergoing star formation, or huge black holes were responsible for most of the universe's early illumination. However, observations from the James Webb Space Telescope suggest that dwarf galaxies played a key role in reionization. Despite their small size, these low-mass galaxies are huge producers of energetic radiation, and their abundance during this period was so substantial that they could transform the entire universe's state.