IPO Update: WORK Medical Technology Readies $13.5 Million U.S. IPO
Summary
- WORK Medical Technology Group has filed proposed terms to raise $13.5 million in a U.S. IPO.
- The firm distributes medical devices and supplies primarily in China.
- WOK has produced sharply declining revenue, a swing to net loss and is exposed to a variety of regulatory and currency depreciation risks.
- My outlook on the IPO is Bearish [Sell].
- Looking for more investing ideas like this one? Get them exclusively at IPO Edge. Learn More »
FreshSplash
What Is WORK Medical Technology Group Ltd?
I previously wrote about WORK’s (WOK) initial IPO filing here.
Since that time, the company has filed a follow-up registration statement detailing its capitalization and proposed IPO terms.
The company distributes various medical devices and supplies in the PRC and overseas.
Management is headed by Chairman and CEO Shuang Wu, who was previously COO of EZGO Technologies (EZGO), a lithium battery and electric bicycle company.
WORK's primary offerings include the following:
Medical face masks
Artery compression tourniquets for bleeding control
Disposable breathing circuits for oxygen and anesthetic gasses
Laryngeal mask airways
Endotracheal tubes
The company sells its products primarily through a network of domestic and export distributors.
Exporters cover a number of large foreign markets, including the United States, Germany, Brazil, Saudi Arabia and other countries.
WORK's IPO Date & Details
The initial public offering date, or IPO, is still to be announced by the company and its IPO underwriter.
(Warning: Compared to stocks with more history, IPOs typically have less information for investors to review and analyze. For this reason, investors should use caution when thinking about investing in an IPO, or immediately post-IPO. Also, investors should keep in mind that many IPOs are heavily marketed, past company performance is not a guarantee of future results and potential risks may be understated.)
WOK intends to sell three million shares of common stock at a proposed midpoint price of $4.50 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $13.5 million, not including the sale of customary underwriter options.
No existing or potentially new shareholders have indicated an interest in purchasing shares at the IPO price.
Assuming a successful IPO at the midpoint of the proposed price range, the company’s enterprise value at IPO (excluding underwriter options) would approximate $62.7 million.
The float to outstanding shares ratio (excluding underwriter options) will be approximately 19.35%. A figure under 10% is generally considered a ‘low float’ stock which can be subject to significant price volatility.
As a foreign private issuer, the company can choose to take advantage of reduced, delayed or exempted financial and senior officer disclosure requirements versus those that domestic U.S. firms are required to follow.
Also, the firm is an ‘emerging growth company’ as defined by the 2012 JOBS Act and may take advantage of reduced public company reporting requirements; prospective shareholders will receive less information for the IPO and in the future as a publicly-held company within the requirements of the Act.
How To Invest In The Company’s Stock: 7 Steps
Investors can buy shares of the stock in the same way they may buy stocks of other publicly traded companies, or as part of the pre-IPO allocation.
Note: This report is not a recommendation to purchase stock or any other security. For investors who are interested in pursuing a potential investment after the IPO is complete, the following steps for buying stocks will be helpful.
Step 1: Understand The Company's Financial History
Although there is not much public financial information available about the company, investors can look at the company's financial history on their form S-1 or F-1 SEC filing (Source).
Step 2: Assess The Company's Financial Reports
The primary financial statements available for publicly-traded companies include the income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows. These financial statements can help investors learn about a company's cash capitalization structure, cash flow trends and financial position.
The company’s recent financial results can be summarized as follows:
Sharply declining topline revenue
Reduced gross profit but increased gross margin
Lowered operating loss but higher negative operating margin
Reduced cash used in operations
As of September 30, 2022, WORK Medical had $731,178 in cash and $14.4 million in total liabilities.
Step 3: Evaluate The Company's Potential Compared To Your Investment Horizon
When investors evaluate potential stocks to buy, it's important to consider their time horizon and risk tolerance before buying shares. For example, a swing trader may be interested in short-term growth potential, whereas a long-term investor may prioritize strong financials ahead of short-term price movements.
Step 4: Select A Brokerage
Investors who do not already have a trading account will begin with the selection of a brokerage firm. The account types commonly used for trading stocks include a standard brokerage account or a retirement account like an IRA.
Investors who prefer advice for a fee can open a trading account with a full-service broker or an independent investment advisor and those who want to manage their portfolio for a reduced cost may choose a discount brokerage company.
Step 5: Choose An Investment Size And Strategy
Investors who have decided to buy shares of company stock should consider how many shares to purchase and what investment strategy to adopt for their new position. The investment strategy will guide an investor's holding period and exit strategy.
Many investors choose to buy and hold stocks for lengthy periods. Examples of basic investing strategies include swing trading, short-term trading or investing over a long-term holding period.
For investors wishing to gain a pre-IPO allocation of shares at the IPO price, they would ‘indicate interest’ with their broker in advance of the IPO. Indicating an interest is not a guarantee that the investor will receive an allocation of pre-IPO shares.
Step 6: Choose An Order Type
Investors have many choices for placing orders to purchase stocks, including market orders, limit orders and stop orders.
Market order: This is the most common type of order made by retail traders. A market order executes a trade immediately at the best available transaction price.
Limit order: When an investor places a buy limit order, they specify a maximum price to be paid for the shares.
Stop order: A buy-stop order is an order to buy at a specified price, known as the stop price, which will be higher than the current market price. In the case of buy-stop, the stop price will be lower than the current market price.
Step 7: Submit The Trade
After investors have funded their account with cash, they may decide an investment size and order type, then submit the trade to place an order. If the trade is a market order, it will be filled immediately at the best available market price.
However, if investors submit a limit order or stop order, the investor may have to wait until the stock reaches their target price or stop-loss price for the trade to be completed.
Thoughts On The IPO
WOK is seeking U.S. public capital market investment for its general growth and working capital requirements.
The company’s financials have shown sharply reduced topline revenue, lowered gross profit but increased gross margin, reduced operating loss but higher negative operating margin, lower cash used in operations.
Free cash flow for the twelve months ending September 30, 2022, was negative ($3.7 million).
Selling expenses as a percentage of total revenue have risen even as revenue has decreased; its Selling efficiency multiple was negative (25.3x) in the most recent year.
The firm currently plans to pay no dividends and to retain any future earnings for reinvestment back into the company's growth and working capital requirements.
WORK Medical is subject to an array of regulations within the PRC and British Virgin Islands regarding conditions under which it may pay dividends.
The firm’s recent capital spending history indicates it has continued to spend on capital expenditures despite negative operating cash flow.
The market opportunity for medical devices in China is expected to grow moderately in the coming years as the population continues to age and demand better healthcare options and treatments.
Like other companies with Chinese operations seeking to tap U.S. markets, the firm operates within a WFOE structure or Wholly Foreign Owned Entity. U.S. investors would only have an interest in an offshore firm with interests in operating subsidiaries, some of which may be located in the PRC. Additionally, restrictions on the transfer of funds between subsidiaries within China may exist.
The Chinese government's crackdown on certain IPO company candidates combined with added reporting and disclosure requirements from the U.S. has put a serious damper on Chinese or related IPOs resulting in generally poor post-IPO performance.
Also, a potentially significant risk to the company’s outlook is the uncertain future status of Chinese company stocks in relation to the U.S. HFCA Act, which requires delisting if the firm’s auditors do not make their working papers available for audit by the PCAOB.
Prospective investors would be well advised to consider the potential implications of specific laws regarding earnings repatriation and changing or unpredictable Chinese regulatory rulings that may affect such companies and U.S. stock listings.
Additionally, post-IPO communications from the management of smaller Chinese companies that have become public in the U.S. has been spotty and perfunctory, indicating a lack of interest in shareholder communication, only providing the bare minimum required by the SEC and a generally inadequate approach to keeping shareholders up-to-date about management’s priorities.
Univest Securities is the sole underwriter and the five IPOs led by the firm over the last 12-month period have generated an average return of negative (34.5%) since their IPO. This is a bottom-tier performance for all significant underwriters during the period.
As for valuation expectations, management is asking IPO investors to pay an Enterprise Value / Revenue multiple of approximately 3.2x.
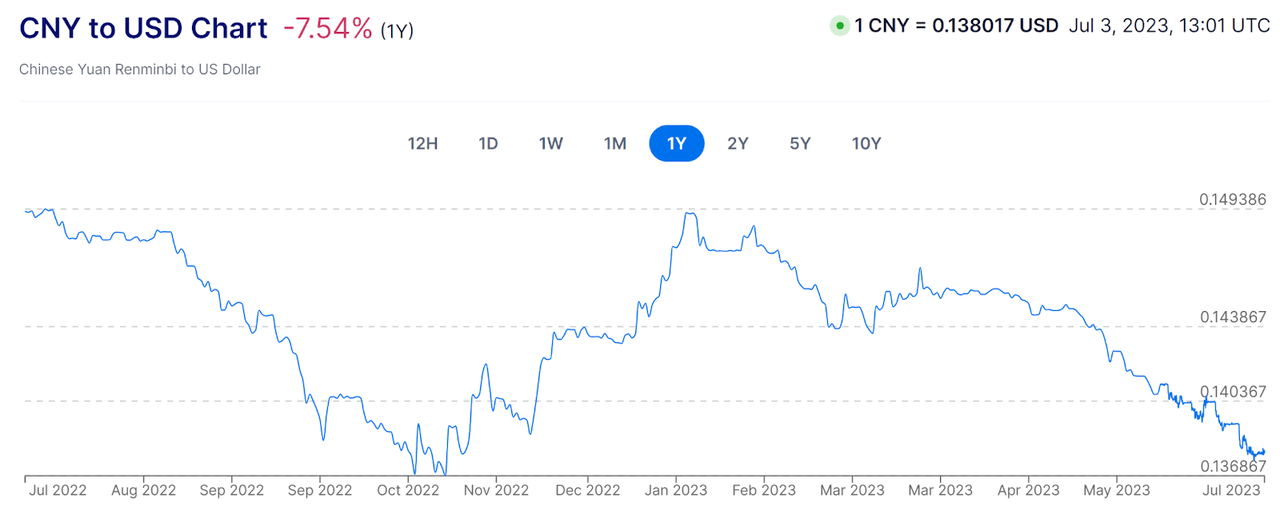
As a result of doing business primarily in China, the company is also subject to currency devaluation of the CNY to the USD, which has dropped around 7.5% over the past year, as the chart shows below:
Given the firm’s sharply dropping topline revenue and gross profit, swing to net loss and attendant regulatory, operational and currency risks operating in the PRC, my outlook on the IPO is Bearish [Sell].
Gain Insight and actionable information on U.S. IPOs with IPO Edge research.
Members of IPO Edge get the latest IPO research, news, and industry analysis.
Get started with a free trial!
This article was written by
I'm the founder of IPO Edge on Seeking Alpha, a research service for investors interested in IPOs on US markets. Subscribers receive access to my proprietary research, valuation, data, commentary, opinions, and chat on U.S. IPOs. Join now to get an insider's 'edge' on new issues coming to market, both before and after the IPO. Start with a 14-day Free Trial.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha's Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.