What is Google Bard? The Big G’s AI chatbot explained
Working Bard on AI. Google's artificial chatbot is rolling out to the public.
There’s been a lot of AI talk in the tech headlines recently, and wants in on the hype. The search brand launched its own AI-powered chatbot called Bard to take on other competitors. Despite sounding like something out of Dungeons and Dragons or Harry Potter, there’s nothing magical about Google’s latest release. Like similar tools, it promises a comprehensive conversation experience, all powered by artificial intelligence.
It’s not the first foray into AI from Google. There are features in Google Docs and Gmail that use AI to predict the ends of sentences. Even the search box on the Google homepage uses AI to predict the end of search queries. There are Google Maps features, Android features, call screening, and dictation apps that all rely on artificial intelligence. The Big G is pretty familiar with all things AI.
But what exactly can Bard do? And how does it all work? We get familiar with Google’s latest AI friend and explain everything that you need to know.
What exactly is Google Bard?
Bard is an AI-powered chatbot released by Google. It uses the brand’s LaMDA language model as a basis for its knowledge. And, unlike other AI chatbots, it’s plugged straight into the web so that it can access fresh, up-to-date information.
What does Bard do with all this knowledge? It uses it to answer questions and queries in a conversational manner. Rather than typing in keywords for a search result, you can actually have a (real) conversation with the chatbot. You can get pretty detailed with these questions, too. Rather than more basic queries such as the year a celebrity was born in, Bard can write out essays or provide programming examples, to name some of its capabilities.
Since LaMDA is a pretty extensive data model, Bard will be restricted to a smaller version. That’s for the moment, at least. Google is first releasing Bard in a testing phase – just like a beta (more on this later on). Google plans to use real-world feedback to improve both the platform and the language model, as well as the brand’s own testing.
At first, Google will restrict access to Bard for “trusted testers”. In the coming weeks, the new AI chatbot will become available to the general public. Google hasn’t mentioned when just yet, but we’d expect it to be within the next four weeks. Bard will also be rolling out into Google Search soon, but the timeline on that is also a little blurry.
How can I get my hands on Bard?
If Bard’s extensive capabilities tickle your fancy, you can get your hands on the AI-powered chatbot. As of 21 March, Google’s waitlist for Bard is open for sign-ups. Those in the US or UK can sign up directly on Google’s Bard site using their regular Google account. The brand will allow users to access the AI tool on a rolling basis, and will email you when it’s your turn.
Once you’ve been granted access to the chatbot, you can get talking to it via the same website. You’ll find a chat window for you to write your prompts, and the platform will walk you through how to get started. You can ask it questions, for help with tasks, or for explanations. Plus, you can even transcribe through your device using the microphone!
Currently, Bard will only respond to certain prompts. Google is being quite protective of its AI baby, and doesn’t want users to go too wild just yet. Like other AI chatbots, don’t expect things to run perfectly smoothly quite so soon.
What can Bard do?
As we’ve lightly touched upon, Google’s Bard can tackle much more complicated questions. Much like current search engines, you’ll be able to ask the AI chatbot regular ol’ questions like “When was Stuff Magazine launched?” and receive accurate information from Bard’s extensive knowledge. But it can go a step further than this.
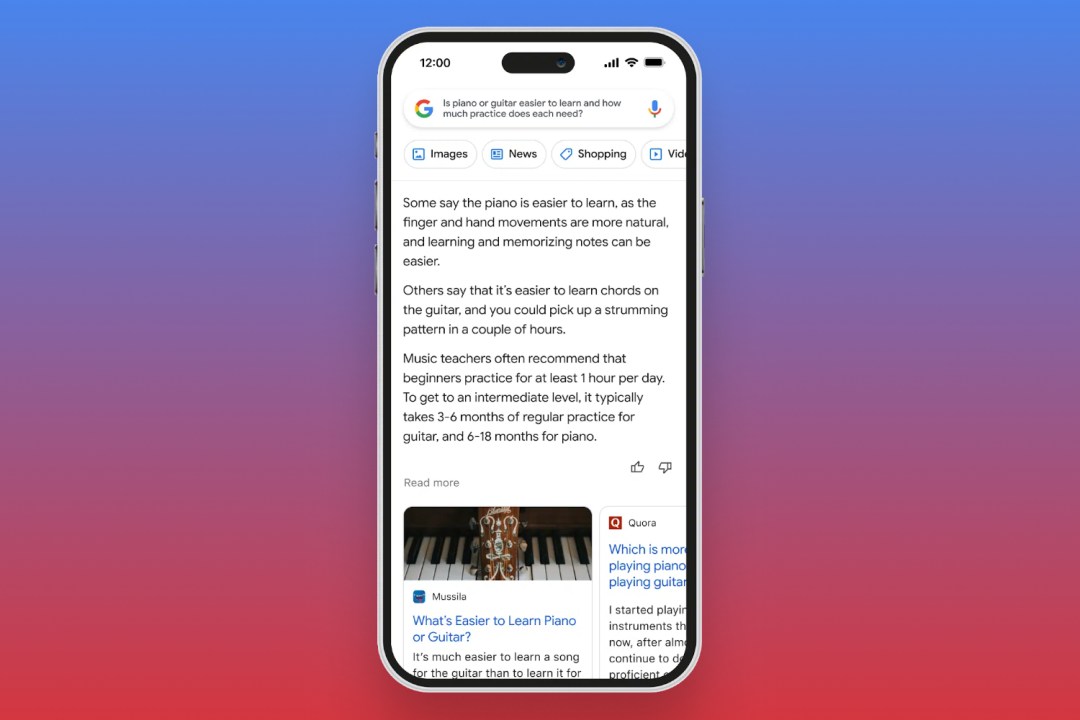
Bard can answer more open-ended or abstract queries, too. It’ll be able to answer questions like “Is the piano or guitar easier to learn?” with lengthy answers. How can it do this? Bard draws data from its language model (which works just like a brain), and the web. This means it’s not only gathering objective facts, but also shared information through blogs and articles. In essence, it can sort of read and understand people’s opinions, which it can use to discuss queries in more detail.

With other AI chatbots, we’ve seen them undertake a variety of different tasks. For example, OpenAI’s ChatGPT has been able to write or plan full-length essays on historical topics. It’s also been able to provide examples of code for programming related questions, and they actually work. It can almost feel like having a mini virtual assistant. The useful kind, though – not like Siri.
Plus, as we mentioned, Google has given Bard free rein to the web. This means it can access up-to-date knowledge, and can adapt as things change. It’ll distill large amounts of information into snippets that are easier to digest. Google also explained these snippets will provide multiple perspectives. However, it looks like Bards’s AI-powered search queries won’t cite sources, which does pose some major reliability issues.
How does Bard compare to other AI chatbots?
On a basic level, Bard is pretty similar to other AI-based chatbots. The core idea is the same – to engage in conversation with the extent of solving queries and questions. Currently, there aren’t too many similar chatbots. ChatGPT is certainly the most advanced, with Replika and ChatSonic bringing up the rear in more basic formats.
These competitors also use extensive training models as a source for knowledge. However, they’re limited to the data in these training models – nothing further. For example, ChatGPT can only access information up to 2021. This means it can get crucial facts wrong in answers, since it can’t access updated information. Bard avoids this issue by plugging straight into the web, where it can access up-to-date data instantly.
But that’s not the only place that Google differs from these other AI chatbots. Google’s data model is far larger than those from competitors, including OpenAI. All the data that Google gathers (which is another can of worms entirely) is used in Bard’s training model. And since Google is one of the largest and most sophisticated data gatherers, Bard’s “brain” is going to be packed with even more valuable information.
Bard’s come along way since Shakespeare
Google’s beta release of its own AI chatbot is hot on the heels of Microsoft’s partnership with OpenAI. ChatGPT is already baked right in to both Bing and Microsoft Edge, and AI features have been in Microsoft Teams for a while now. While Google has been working on LaMDA for years, Bard’s sudden release at the moment is certainly some form of response to the competition.
With Bard’s superior knowledge base and access to the web, it faces great odds of making a better AI chatbot. Your days of trawling through search results could soon be over.


