During UN climate talks, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced that India would aim for net zero emissions by 2070 – two decades later than many proponents had hoped. He also slightly revised some of his existing targets by promising that India will install 500 gigawatts of non-fossil energy by 2030 and by that date will meet half of its energy needs from renewable sources, against a previously announced 40 percent target . Read here the energy needs of India and the share of solar power and other renewables …
With Prime Minister Narendra Modi announcing India’s intention to reach 500 GW of its capacity through non-fossil fuels and 50% of its energy needs from renewable energy by COP26 by 2030, the countdown has begun with the ambitious target.
Leaders have begun meeting in government to draw up a detailed action plan to include the 450 GW to 500 GW plan announced by Prime Minister Modi at COP26 as it is not a common target, experts say
India’s capacity for renewable energy (RE) is at just around 100 GW by 2021. This means that by 2030 the country should add another 400 GW, officials said.
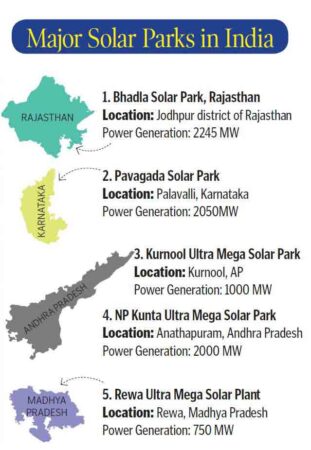
India’s Solar Initiatives
- Solar energy has taken a central place in India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change with the National Solar Mission as one of the key missions.
- National Solar Mission (NSM) launched at 11ste January 2010. Its goal is to establish India as a world leader in solar energy by creating the policy conditions for solar technology diffusion across the country as quickly as possible.
- It aims to install 100 GW of grid-connected solar power plants by the year 2022. This is in line with India’s Intended National Fixed Contributions (INDCs) target to achieve approximately 40% cumulative electric power installed capacity of non-fossil.
- To achieve the above target, the Government of India has launched various schemes to encourage the generation of solar power in the country, such as Solar Park Scheme, Channel Bank and Channel Top Scheme, Bundle Scheme, Connected Solar Power Roof Scheme, etc.
- India has an ambitious cross-border power network plan—‘One Sun One World One Grid’– which seeks to transmit solar power generated in one region to meet the electricity needs of others

Source: Telangana Today