Diagnosis and management of bone infections in children: PIDS-IDSA guideline
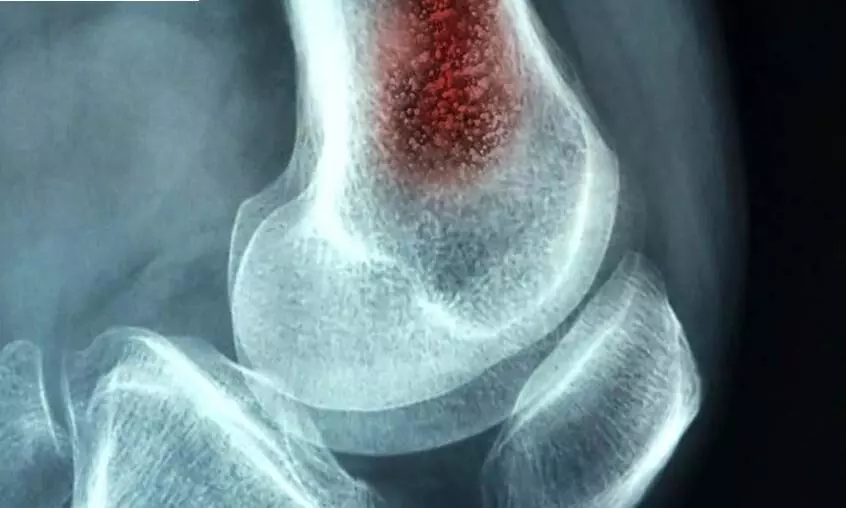
USA: The Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society (PIDS) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) have released a new guideline for the diagnosis and management of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in pediatric patients.
According to the guideline, invasive diagnostic tests play an important role in the treatment of bone infections in children, but these tests may not always be necessary or feasible.
The clinical practice guideline, published in the Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, is the first-ever developed on the diagnosis and management of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in pediatric patients.
These infections occur when bacteria in the blood enter the bone and spreads, causing symptoms such as pain, fever, a limp, or swelling, and can lead to serious, disabling complications if not treated appropriately. Bone specimens or other samples can help confirm the type of bacteria causing an infection and the appropriate antibiotics for treatment. The new guideline recommends such testing but acknowledges that collecting these specimens, which may involve invasive surgical procedures requiring sedation or anesthesia, often may not be possible.