Abdominal Skin Punch Biopsy - Highly Sensitive Diagnostic Procedure for Systemic Amyloidosis: Study
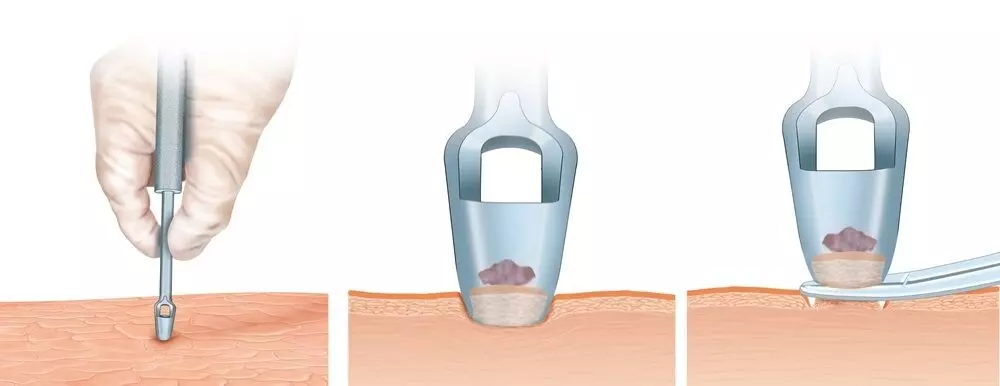
Abdominal Skin Punch Biopsy is sensitive for diagnosing Systemic amyloidosis & can be improved with adequate biopsy depth and diameter, finds a new study.
Early and accurate diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis (SA) is critical for optimal patient outcomes. Biopsy of clinically uninvolved skin and subcutaneous tissue including abdominal skin punch biopsy (ASPB) is often used as a surrogate for affected organ sampling.
There is a lack of published data on the sensitivity and specificity of ASPB for diagnosing systemic amyloidosis (SA).
Although biopsy of clinically involved organs in systemic amyloidosis (SA) is the gold standard for diagnosis, it carries risks of complications. Although less-invasive, abdominal fat pad aspiration (AFPA) may yield small amounts of tissue, require multiple aspirations, and depend upon some technical experience.
In amyloidosis symptoms differ in each case depending on the organ system that is affected. During an Abdominal Skin Punch Biopsy, a circular tool is used to remove the deeper layers of the skin from the abdominal region. A recent study was conducted to check the sensitivity and specificity of ASPB for diagnosing SA.
The study was a retrospective review of all the abdominal skin punch biopsies performed between 2000 and 2020 to diagnose systemic amyloidosis. Amyloid deposition was confirmed by Congo red stain. Study group included patients with histopathologically and clinically confirmed diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. Control group includes patients without histopathology of amyloid deposition and no clinical systemic amyloidosis.
Forty-one patients meeting inclusion criteria were analyzed; 23 study group and 18 control group patients. The overall diagnostic sensitivity of ASPB was 43% and the specificity 100%. The AL amyloidosis diagnostic sensitivity was 64%. ASPB >10 mm in depth had 100% sensitivity compared to 24% for depth ≤10 mm.
The study clearly shows that abdominal skin punch biopsy (ASPB) is a minimally invasive and highly specific method of diagnosing systemic amyloidosis (SA).
"It is particularly sensitive for diagnosing AL amyloidosis and the diagnostic sensitivity can be significantly improved with adequate biopsy depth and diameter," the investigators concluded.
Reference:
Study titled, "Utility of abdominal skin punch biopsy for detecting systemic amyloidosis," as published in the Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.
Next Story