Start Java Flight Recorder Eclipse Profile Monitor
Java Flight Recorder in Eclipse
JDK Mission Control provides a powerful suite of tools for developers and DevOps professionals to profile their applications and monitor the performance of the JVM. But without a Java Flight Recorder data file to analyze, JDK Mission Control is feckless. In this Java Flight Recorder in Eclipse tutorial, we will show you three simple ways to start a recording and view the automated analysis result.
Flight Recorder Example Prerequisites
This JDK Flight Recorder example assumes the following prerequisites:
- JDK 11 is installed and JAVA_HOME is set
- A 2020 Eclipse IDE release is being used
- The Java Mission Control Eclipse plugin is configured
It’s worth noting that only one of the three examples of how to start Java Flight Recorder require the Eclipse plugin to be installed. Use of JVM arguments and the use of the Java Diagnostic Command only require a recent Java installation.
Mission Control’s JVM browser
The easiest way to start Java Flight Recorder in Eclipse is to start a Java application and then move to the JDK Mission Control perspective. All of the running JVMs on your computer will be listed.
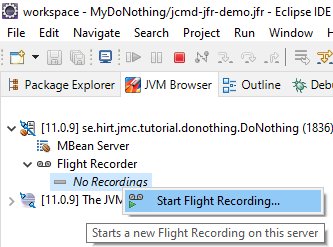
The JVM Browser view is the easiest way to start the Java Flight Recorder in Eclipse.
Simply right-click on the Flight Recorder and choose the Start Flight Recording option. A window asking when to start the flight recording and how long to record for will open. Customize the Flight Recorder accordingly and then run the monitoring process. When Flight Recorder finished, the results will appear in the Java Mission Control window.
Flight Recorder JVM settings
This second way to start Java Flight Recorder in Eclipse will work even if you do not have the Java Mission Control plugin installed.
You can always start a flight recording when you run a Java application simply by editing the JVM arguments and adding the StartFlightRecording flag. Save these Flight Recorder JVM settings in an Eclipse launch configuration, and a recording will start every time you run the application.
The following String attribute added to an Eclipse launch configuration will recording the JVM for 200 seconds, starting after a 5 second delay:
<stringAttribute key="org.eclipse.jdt.launching.VM_ARGUMENTS"
value="-Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -XX:+FlightRecorder -XX:FlightRecorderOptions=stackdepth=128 -XX:+UnlockDiagnosticVMOptions -XX:+DebugNonSafepoints -XX:StartFlightRecording=delay=2s, duration=40s, name=StartFlightRecorder, filename=${workspace_loc}/recordings/flight-recording.jfr" />
Flight Recorder and jcmd
The third way to start Java Flight Recorder in eclipse is to open your Eclipse project in a DOS prompt or a BASH terminal and run the Java Diagnostics Command jcmd.
So long as the JDK’s bin directory is on the classpath, you can run the jcmd command from any directory. Without any switches, the command will list the process id of any running JVM on your computer.
MissionControl@EXAMPLE /c/tutorial/jmc (master) $ jcmd 15308 jdk.jcmd/sun.tools.jcmd.JCmd 1836 se.hirt.jmc.tutorial.donothing.DoNothing
With knowledge of the JVM process ID in hand, you can use jcmd to start the flight recorder:
MissionControl@EXAMPLE /c/tutorial/jmc (master) $ jcmd 15308 jdk.jcmd/sun.tools.jcmd.JCmd 1836 se.hirt.jmc.tutorial.donothing.DoNothing
How to start Java Flight Recorder
In review, the three easiest ways to start the Java Flight Recorder in Eclipse are:
- Use the Java Mission Control plugin’s JVM browser view to start JVM profiling
- Create an Eclipse launch configuration file and set the StartFlightRecorder VM argument
- Use the Java Diagnostic Command, jcmd, to start Java Flight Recordings.
When the flight recordings are complete, they can be opened with Java Mission control. JVM analysis and performance troubleshooting simply couldn’t be made easier.



