TV star Zarina Roshan Khan aka Indu Dadi passes away due to cardiac arrest. Here's why sudden cardiac arrests happen
Serum Institute, Bharat Biotech to begin trial of intranasal COVID-19 vaccine soon
Samsung's #FullOnFestival is almost here!
High levels of ultraviolet light 'most strongly' associated with reduced growth of COVID-19
Millions more virus rapid tests, but are results reported?
TV star Zarina Roshan Khan aka Indu Dadi passes away due to cardiac arrest. Here's why sudden cardiac arrests happen
TV star Zarina Roshan Khan aka Indu Dadi passes away due to cardiac arrest. Here's why sudden cardiac arrests happen
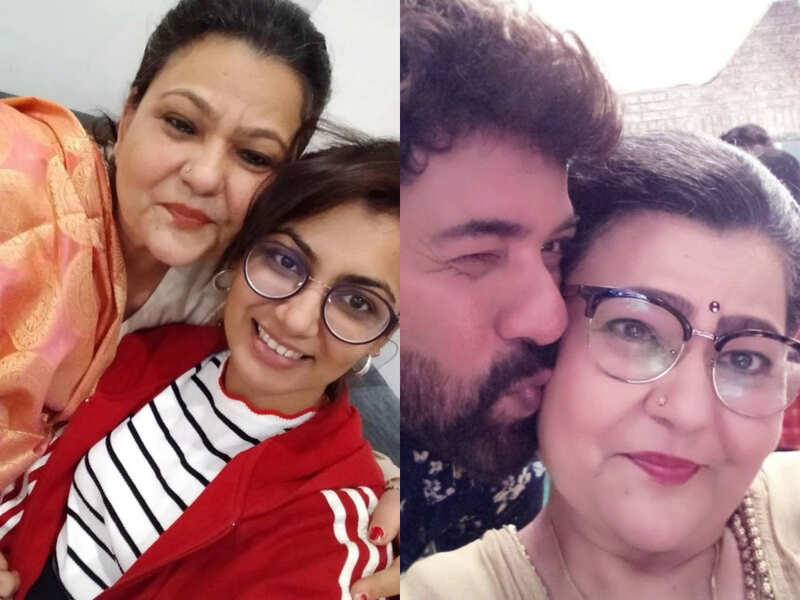

The world of television bid adieu to TV actress, Zarina Roshan Khan, who passed away after an unfortunate cardiac arrest recently.
The actress, who was fondly remembered for her role in the show 'Kumkum Bhagya' as Indu Dadi was just 54.
While tributes for the actress are pouring in from her fans and celebrities, it has been reported that her health deteriorated quite suddenly, triggering a cardiac arrest which made her lose her life.
What does a cardiac arrest mean?
A cardiac arrest means a condition when blood flow to the heart stops all of a sudden, causing an imbalance. It is also termed as an abrupt cause of heart function, breathing and consciousness.
While cardiac arrests often disrupt body functioning, it can turn fatal if timely action is not taken. When the heart stops functioning, there is a loss of blood supply to the brain, lungs and other vital organs, which is routed through the heart. It can also result in a loss of consciousness and pulse.
Signs and symptoms to know about
The most striking thing about cardiac arrests is that it can occur to anyone, regardless of their health or prevalent heart ailment history. Though sudden cardiac arrests often occur without warning signs, there are some simple symptoms which demand acute attention:
-Shortness or loss of breathing
-Not feeling a pulse
-Feeling discomfort or pain around the chest
-Sudden collapse
-Excessive palpitations
-Profuse sweating
-Weakness
-Rapid or irregular heartbeats
If any of these signs are spotted, immediate medical consultation is advised.
Is cardiac arrest the same as a heart attack?
While both conditions affect heart functioning, they are often confused to be the same, which is wrong.
Heart attacks are usually caused when a sudden blockage in the heart stops its functioning, causing death of the heart muscle tissue and blocking essential blood flow. Also referred to as myocardial infarction, the risk for a heart attack is also high for those with pre-existing health conditions, lifestyle problems or genetic history. While heart attacks are just as serious as cardiac arrests, they are less fatal and can be treated well, with the advancement of medical technology.
Unlike this, a cardiac arrest happens when the heart's electrical system, which is responsible for pumping blood supply and make the heartbeat gets corrupted and "stops" heart functioning in its entirety. In some cases, a cardiac arrest can also be triggered by erratic arrhythmias and problems with ventricular fibrillation. If proper steps aren't taken in the first few minutes post a cardiac arrest, there is a high risk of loss of life.
It should be known that while heart attacks and cardiac arrests are used interchangeably, sometimes, a heart attack can trigger a sudden cardiac arrest as well. Cardiac arrests can also strike a person in recovery from a heart attack.
Apart from this, conditions like congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathy (problem caused by an enlarged heart), coronary artery disease, valvular trouble are also linked to an increased risk of developing sudden cardiac arrest.
How is a cardiac arrest treated?
While sudden cardiac arrests can be extremely fatal, the first few minutes post the attack can turn out to be the most crucial as important steps taken during this time period can help aid recovery and save a person's life. This is all the more important if the victim is unconscious, is not breathing well or has no pulse.
In cases of cardiac arrests, emergency care numbers should be contacted without delay. In the waiting time, providing rescue CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) can save a person's life. Pushing the person's chest fast and hard, providing compressions and rescue breathing which would 'unblock' the airways can provide respite. However, compressions need to be done fast. Statistics suggest that emergency CPR can double or triple a person's survival odds.
Using a defibrillator is another way to resuscitate heart functioning. The external portable machine essentially shocks the body into pumping oxygenated blood back to the vitals, reviving functioning and making a person gain back lost consciousness. In extreme cases, the debrifilator can be used repeatedly, until more medical help can be provided.
The actress, who was fondly remembered for her role in the show 'Kumkum Bhagya' as Indu Dadi was just 54.
While tributes for the actress are pouring in from her fans and celebrities, it has been reported that her health deteriorated quite suddenly, triggering a cardiac arrest which made her lose her life.
What does a cardiac arrest mean?
A cardiac arrest means a condition when blood flow to the heart stops all of a sudden, causing an imbalance. It is also termed as an abrupt cause of heart function, breathing and consciousness.
While cardiac arrests often disrupt body functioning, it can turn fatal if timely action is not taken. When the heart stops functioning, there is a loss of blood supply to the brain, lungs and other vital organs, which is routed through the heart. It can also result in a loss of consciousness and pulse.
Signs and symptoms to know about
The most striking thing about cardiac arrests is that it can occur to anyone, regardless of their health or prevalent heart ailment history. Though sudden cardiac arrests often occur without warning signs, there are some simple symptoms which demand acute attention:
-Shortness or loss of breathing
-Not feeling a pulse
-Feeling discomfort or pain around the chest
-Sudden collapse
-Excessive palpitations
-Profuse sweating
-Weakness
-Rapid or irregular heartbeats
If any of these signs are spotted, immediate medical consultation is advised.
Is cardiac arrest the same as a heart attack?
While both conditions affect heart functioning, they are often confused to be the same, which is wrong.
Heart attacks are usually caused when a sudden blockage in the heart stops its functioning, causing death of the heart muscle tissue and blocking essential blood flow. Also referred to as myocardial infarction, the risk for a heart attack is also high for those with pre-existing health conditions, lifestyle problems or genetic history. While heart attacks are just as serious as cardiac arrests, they are less fatal and can be treated well, with the advancement of medical technology.
Unlike this, a cardiac arrest happens when the heart's electrical system, which is responsible for pumping blood supply and make the heartbeat gets corrupted and "stops" heart functioning in its entirety. In some cases, a cardiac arrest can also be triggered by erratic arrhythmias and problems with ventricular fibrillation. If proper steps aren't taken in the first few minutes post a cardiac arrest, there is a high risk of loss of life.
It should be known that while heart attacks and cardiac arrests are used interchangeably, sometimes, a heart attack can trigger a sudden cardiac arrest as well. Cardiac arrests can also strike a person in recovery from a heart attack.
Apart from this, conditions like congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathy (problem caused by an enlarged heart), coronary artery disease, valvular trouble are also linked to an increased risk of developing sudden cardiac arrest.
How is a cardiac arrest treated?
While sudden cardiac arrests can be extremely fatal, the first few minutes post the attack can turn out to be the most crucial as important steps taken during this time period can help aid recovery and save a person's life. This is all the more important if the victim is unconscious, is not breathing well or has no pulse.
In cases of cardiac arrests, emergency care numbers should be contacted without delay. In the waiting time, providing rescue CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) can save a person's life. Pushing the person's chest fast and hard, providing compressions and rescue breathing which would 'unblock' the airways can provide respite. However, compressions need to be done fast. Statistics suggest that emergency CPR can double or triple a person's survival odds.
Using a defibrillator is another way to resuscitate heart functioning. The external portable machine essentially shocks the body into pumping oxygenated blood back to the vitals, reviving functioning and making a person gain back lost consciousness. In extreme cases, the debrifilator can be used repeatedly, until more medical help can be provided.
End of the article
Comments (0)
Featured in Lifestyle

Constipation in children: Why it should be taken seriously

Be the supportive mother-in-law for your daughter

Is India heading towards a second wave of Coronavirus? Here's all you need to know

Kajol's yellow printed kurta with pants design is perfect for the festive season

TV star Zarina Roshan Khan aka Indu Dadi passes away due to cardiac arrest. Here's why sudden cardiac arrests happen

Know the best time to get pregnant, according to your zodiac sign

COVID-19: How to determine which activity is safe and which is worth skipping

These zodiac signs will be affected the most by the full moon Halloween

5 ways to get that perfect smile
LATEST VIDEOS
Health-Fitness
 Avoid 'doomscrolling' in these times. Here's why02:55
Avoid 'doomscrolling' in these times. Here's why02:55 Jayaka Yagnik shows us simple asanas that can help us to get fitter for the festive season01:44
Jayaka Yagnik shows us simple asanas that can help us to get fitter for the festive season01:44 7 yoga poses to prevent breast cancer03:01
7 yoga poses to prevent breast cancer03:01![[Level 2-4+] Bodyweight VS Weights! Choose your side](https://static.toiimg.com/photo/34824568.cms) [Level 2-4+] Bodyweight VS Weights! Choose your side07:00
[Level 2-4+] Bodyweight VS Weights! Choose your side07:00 Fitness expert Ruju Desai shows us 3 simple abs exercises that can be done at home02:01
Fitness expert Ruju Desai shows us 3 simple abs exercises that can be done at home02:01 Guide Level 3-4 Fat-Burning Intensive Workout42:43
Guide Level 3-4 Fat-Burning Intensive Workout42:43 Yoga practitioner Iti Jain shares ways to beat anxiety through yoga06:05
Yoga practitioner Iti Jain shares ways to beat anxiety through yoga06:05 Global Handwashing Day: Here's why washing your hands will keep COVID-19 at bay00:46
Global Handwashing Day: Here's why washing your hands will keep COVID-19 at bay00:46 The best time to walk for weight loss 00:42
The best time to walk for weight loss 00:42 6 effective exercises to lose face fat05:29
6 effective exercises to lose face fat05:29
StoriesSEE All





























































![[Level 2-4+] Bodyweight VS Weights! Choose your side [Level 2-4+] Bodyweight VS Weights! Choose your side](https://static.toiimg.com/thumb/msid-78730478,imgsize-631194,width-166,height-124/78730478.jpg)



















![[Gym] Leg Training (voice-over with tips)
[Gym] Leg Training (voice-over with tips)](https://static.toiimg.com/thumb/77056786.cms?width=147&height=86)





![[Level 2-4+] Bodyweight VS Weights! Choose your side](https://static.toiimg.com/thumb/imgsize-631194,msid-78730478,width-200,resizemode-4/78730478.jpg)










closecomments
SIGN IN WITH
FacebookGoogleEmail