Pointing out that inflation is higher than expected, former RBI deputy governor Viral Acharya had on August 1 said the rate-setting panel of the RBI should "respect" its core mandate of controlling inflation at its upcoming policy review meet.
India's average retail inflation for the last two quarters (January-March and April-June) came in at above 6 percent. If retail inflation for the current quarter (July-September 2020) also crosses the 6 percent limit, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) would miss its inflation-targeting mandate.
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), the RBI's rate-setting panel headed by Governor Shaktikanta Das, is scheduled to meet from August 4-6 to review key policy rates and take a decision accordingly.
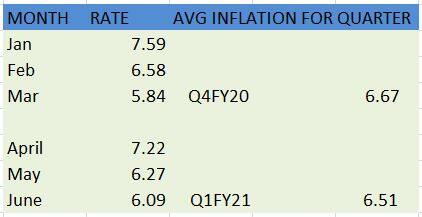 Source: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
Source: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
Pointing out that inflation is higher than expected, former RBI deputy governor Viral Acharya had on August 1 said the rate-setting panel of the RBI should "respect" its core mandate of controlling inflation at its upcoming policy review meet.
RBI's inflation-targeting approach
The RBI has adopted the inflation-targeting framework as the basis of its monetary policy. Four years back, it amended the RBI Act 1934 in order to provide a statutory basis for the implementation of the inflation-targeting approach.
Accordingly, the Centre had set a 4 percent Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation as the target for the period from August 5, 2016 to March 31, 2021. An upper tolerance limit of 6 percent and a lower tolerance limit of 2 percent was set. If the CPI inflation goes beyond the 2 percent to 6 percent range on either side, for three consecutive quarters, the central bank is deemed to have missed its target.
The RBI is then required to provide a detailed report to the Centre outlining the reasons for its failure to achieve the inflation target and the remedial actions proposed to be taken. The report must also have an estimated time-frame within which the central bank says the inflation target can be achieved thereafter.
In the current scenario, if the MPC decides on yet another rate cut, it could risk missing its inflation-targeting mandate. In the March policy meet, the committee had slashed repo rate by 75 basis points (bps), followed by another 40 bps trim in the May off-cycle meet amid the COVID-19 pandemic. However, as per several reports, the RBI may resort to a rate cut amid concerns around India's economic outlook that has been dealt a harsh blow by the coronavirus pandemic.
Read More | RBI MPC meet Aug 4-6: What happened at policy meets earlier in 2020
Repo rate and inflation
Repo rate is one among the several direct and indirect monetary policy instruments used by the central bank and is used to control inflation and spur growth. It is the rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks.
In simple terms, the repo rate and inflation share an inverse relationship. In the event that the RBI wishes to bring down inflation, it increases the repo rate, making it expensive for banks to borrow, thus disincentivising the same.