 Honeywell Quantum computer inside the chamber. (Image: Honeywell)
Honeywell Quantum computer inside the chamber. (Image: Honeywell)
Back in March, Honeywell said that it would make the world’s most powerful quantum computer “within the next three months”. Fast forward to June and the multinational conglomerate delivers on its promise with the launch of a system that features a quantum volume of 64— twice as powerful as the next fastest system.
Quantum computing refers to the use of quantum-mechanical phenomena (superposition and entanglement) to perform computation. The quantum volume is a measurement that takes into account the number of quantum bits (or qubits) of a machine as well as their connectivity and error rates.
Tony Uttley, the President of Honeywell Quantum Solutions, said, “What makes our quantum computers so powerful is having the highest quality qubits, with the lowest error rates. This is a combination of using identical, fully connected qubits and precision control.”
What are quantum computers?
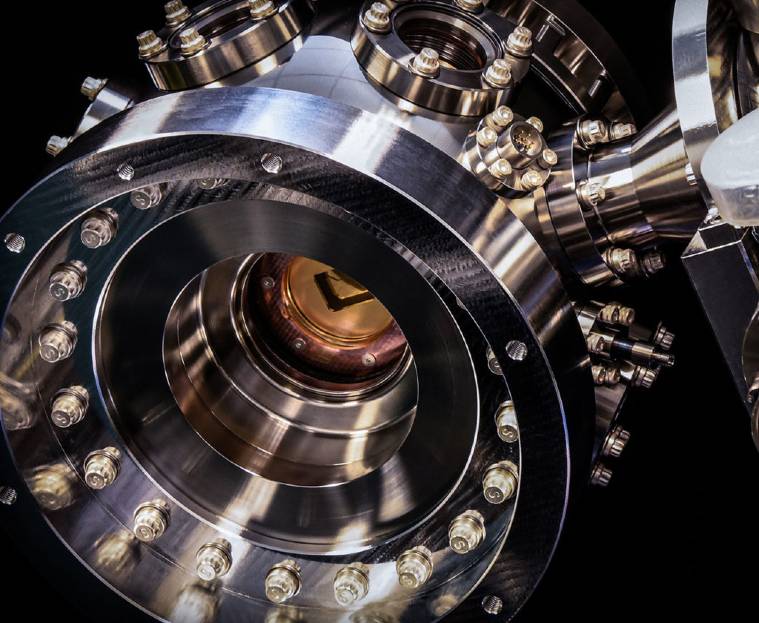 The world’s highest-performing Quantum Computer is here. (Image: Honeywell)
The world’s highest-performing Quantum Computer is here. (Image: Honeywell)
Quantum computers are believed to be able to solve computational problems faster than classical computers and promise to outperform even the most capable of present and future supercomputers. To envision what a quantum computer looks like, Tony says to imagine computers from 60 years ago which would take up a full room and have wires running everywhere.
Quantum computers investigate many potential outcomes at the same time. While traditional computing bits are in a state of either “0” or “1”, the qubits of a quantum system can be in both states at the same time. This property of a quantum computer is called superposition.
Also read | Explained: What is quantum supremacy?
“That means that when you have these qubits interacting with each other in a computation, you get, what I call, a quantum superpower,” Tony said. “You get an exponential expansion in the number of values that can all be considered at the same time.”
The Honeywell quantum system
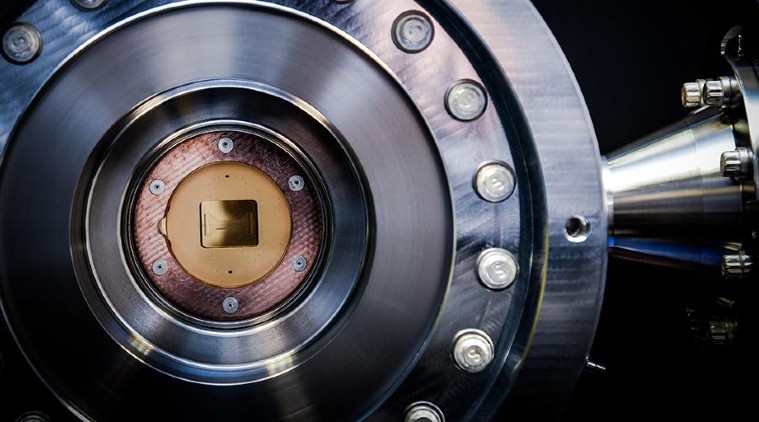
The core of the Honeywell system is an ultra-high vacuum chamber. It is a stainless steel sphere, about the size of a basketball with portals to allow in laser light, and from which the air has been pumped out such that it contains a vacuum of five times fewer particles than outer space. There are ion traps inside the chamber, each of which is the size of a small coin (24.3 mm). The ion plays the role of a qubit. The chamber is cryogenically cooled with liquid helium to bring the temperature of the iron trap chip to 10 degrees above absolute zero (-262.7 °C).
The ion traps are controlled by a laser, which is aimed at trapping the charge from outside the sphere through a small glass window. “Within the chamber, electric fields levitate individual atoms 0.1 mm above an ion trap, a silicon chip covered in gold about the size of a quarter. Scientists shine lasers at these positively charged atoms to perform quantum operations,” Honeywell said in a post.
Express Tech is now on Telegram. Click here to join our channel (@expresstechnology) and stay updated with the latest tech news
According to the company, the main focus while building the quantum computer was to eliminate the errors present within the system on smaller numbers of qubits and then working to scale up their number. Low errors in the quantum operations expand the quantum volume, thus increasing the capability of quantum computing.