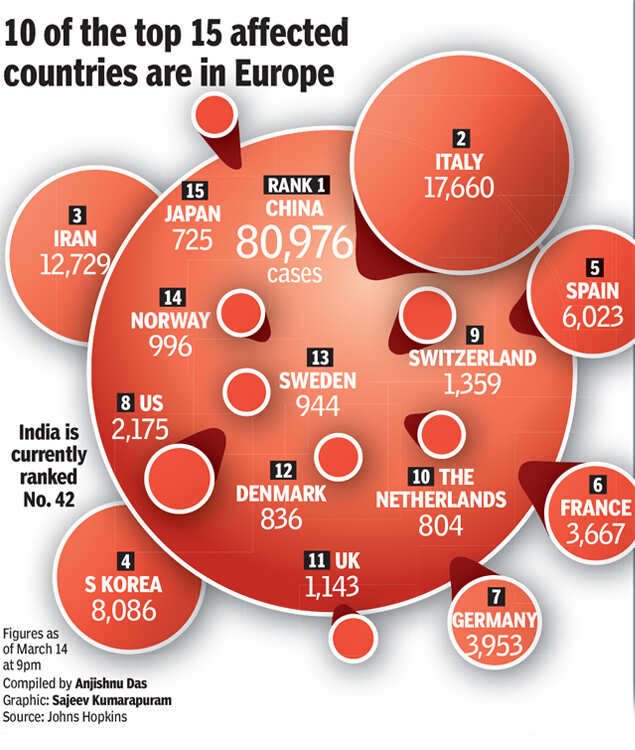
NEW DELHI: The total number of coronavirus cases across the world continues to rise. As many as 10 of the top 15 affected countries are in Europe. Fortunately, in India, community spread remains limited. In almost 90% of cases in India, the infected person has contracted the disease while abroad. There have been only a few cases of local transmission, which means India is still in Stage II of an epidemic. Here's a look at various stages of epidemic and what can be done to keep COVID-19 in check.
STAGE I: Early cases are primarily imported from affected countries.
STAGE II: Local transmission begins from positive cases. Transmission is limited to people who have come in direct contact with an infected individual with travel history.
STAGE III: There is large-scale spread in community. Transmission is occurring in patients who have had no direct contact with Covid-19 patients with travel history. It is spreading in community and affecting larger clusters.
STAGE IV: The disease takes shape of a nationwide epidemic with no clear endpoint. Italy, for example, is in this stage.
How to keep yourself and your family safe
➤ Maintain a six-foot distance from people who cough. This is because droplets carry the virus and could land in the mouths or noses of passersby.
➤ Don’t touch your eyes, nose, and mouth.
➤ Stay home when sick.
➤ Use a tissue to cover your mouth while coughing. Throw the tissue in the trash.
➤ Disinfect frequently touched objects (lift buttons, door knobs, restaurant tables) with household cleaning spray or wipes.
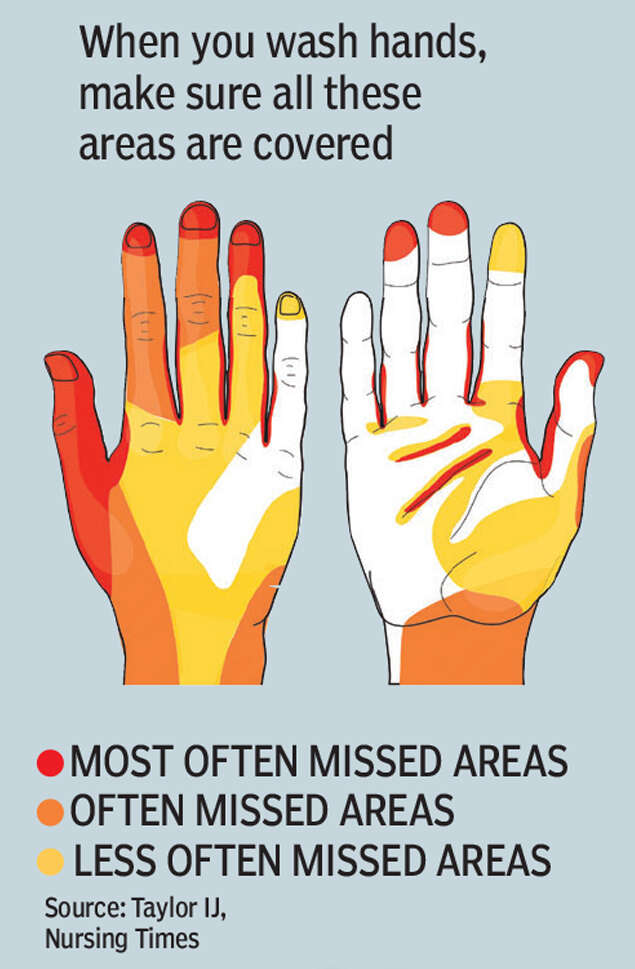
➤ Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds .
➤ Use alcohol-based sanitisers.
How the virus spreads
People are thought to be most contagious when they are most symptomatic (the sickest). But even those without symptoms could spread the virus. Infection is possible if a person touches a surface or object that has the virus on it and then touches his or her mouth, nose, or eyes. The virus is supposedly heavier than common ones, so it can’t travel more than three feet or so.
How symptoms of COVID-19 compare to those of other diseases
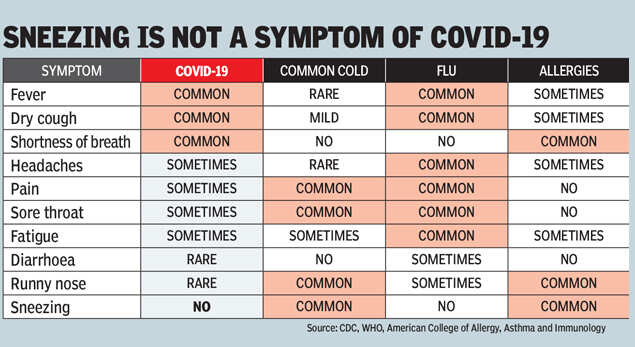
Source: CDC, WHO, American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology
Compiled by Anjishnu Das

STAGE I: Early cases are primarily imported from affected countries.
STAGE II: Local transmission begins from positive cases. Transmission is limited to people who have come in direct contact with an infected individual with travel history.
STAGE III: There is large-scale spread in community. Transmission is occurring in patients who have had no direct contact with Covid-19 patients with travel history. It is spreading in community and affecting larger clusters.
STAGE IV: The disease takes shape of a nationwide epidemic with no clear endpoint. Italy, for example, is in this stage.
How to keep yourself and your family safe
➤ Maintain a six-foot distance from people who cough. This is because droplets carry the virus and could land in the mouths or noses of passersby.
➤ Don’t touch your eyes, nose, and mouth.
➤ Stay home when sick.
➤ Use a tissue to cover your mouth while coughing. Throw the tissue in the trash.
➤ Disinfect frequently touched objects (lift buttons, door knobs, restaurant tables) with household cleaning spray or wipes.
➤ Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds .
➤ Use alcohol-based sanitisers.
How the virus spreads
People are thought to be most contagious when they are most symptomatic (the sickest). But even those without symptoms could spread the virus. Infection is possible if a person touches a surface or object that has the virus on it and then touches his or her mouth, nose, or eyes. The virus is supposedly heavier than common ones, so it can’t travel more than three feet or so.

More on Covid-19
How symptoms of COVID-19 compare to those of other diseases

Source: CDC, WHO, American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology
Compiled by Anjishnu Das
Download The Times of India News App for Latest India News.
Coronavirus outbreak
Trending Topics
LATEST VIDEOS
More from TOI
Navbharat Times
Featured Today in Travel
Quick Links
Coronavirus in MumbaiCoronavirus in KolkataCoronavirus in HyderabadCoronavirus in DelhiCoronavirus in BangaloreCoronavirus symptomsCoronavirus in IndiaWhat is CoronavirusCoronavirus NewsSolar EclipseNPRWhat is NRCCAB BillCAB and NRCRTI BillPodcast newsLok SabhaShiv SenaYSRCPCongressBJP newsUIDAIIndian ArmyISRO newsSupreme Court
Get the app









