Written by Paul Mozur
The Chinese government has drawn wide international condemnation for its harsh crackdown on ethnic Muslims in its western region, including holding as many as 1 million of them in detention camps.
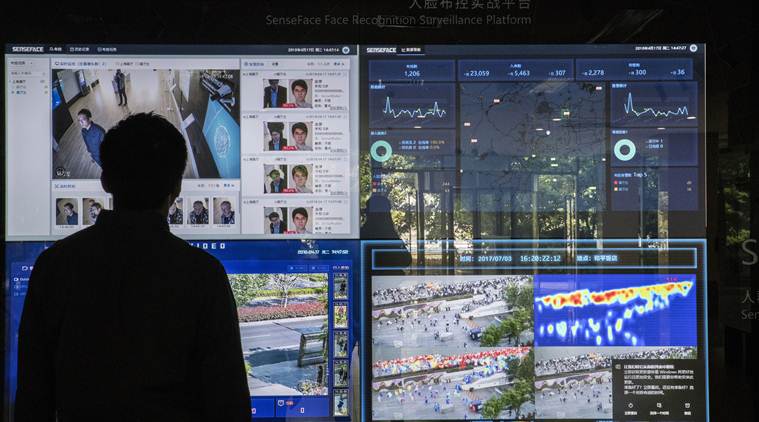
Now, documents and interviews show that authorities are also using a vast, secret system of advanced facial recognition technology to track and control the Uighurs, a largely Muslim minority. It is the first known example of a government intentionally using artificial intelligence for racial profiling, experts said.
The facial recognition technology, which is integrated into China’s rapidly expanding networks of surveillance cameras, looks exclusively for Uighurs based on their appearance and keeps records of their comings and goings for search and review. The practice makes China a pioneer in applying next-generation technology to watch its people, potentially ushering in a new era of automated racism.
The technology and its use to keep tabs on China’s 11 million Uighurs were described by five people with direct knowledge of the systems, who requested anonymity because they feared retribution. The New York Times also reviewed databases used by the police, government procurement documents and advertising materials distributed by the AI companies that make the systems.

Chinese authorities already maintain a vast surveillance net, including tracking people’s DNA, in the western region of Xinjiang, which many Uighurs call home. But the scope of the new systems, previously unreported, extends that monitoring into many other corners of the country.
Police are now using facial recognition technology to target Uighurs in wealthy eastern cities like Hangzhou and Wenzhou and across the coastal province of Fujian, said two of the people. Law enforcement in the central Chinese city of Sanmenxia ran a system that over the course of a month this year screened whether residents were Uighurs 500,000 times.
A new generation of startups catering to Beijing’s authoritarian needs are beginning to set the tone for emerging technologies like artificial intelligence. Similar tools could automate biases based on skin color and ethnicity elsewhere.
“Take the most risky application of this technology, and chances are good someone is going to try it,” said Clare Garvie, an associate at the Center on Privacy and Technology at Georgetown Law.