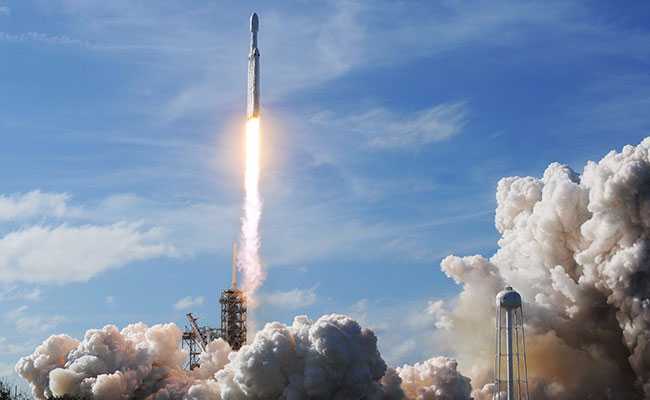
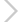
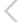
New Delhi: SpaceX chief executive Elon Musk today sent Falcon Heavy, the world's most powerful rocket, which is loaded with his red Tesla roadster toward an orbit near Mars. It is the first time that a rocketing firm has managed to guide at least two of the Falcon Heavy's first-stage rocket boosters to land upright back on Earth. Also it's the first time that a car is being sent to the space. At the wheel of the sports car is a dummy dressed in a spacesuit nicknamed Starman and the words "DON'T PANIC" visible on the dashboard.
A a look at some of the other space projects by Tesla CEO Elon Musk:
- Rockets on Earth: Elon Musk's vision is to make New York to Shanghai travel via rocket accessible in just about half an hour. Elon Musk said that BFR will be the vehicle that would fly to most places on Earth in under 30 minutes and anywhere in under an hour. The cost per seat would be about the same as an airplane economy fare, he said.
- Reusable rockets: One of the key goals of Elon Musk is to make rockets as reusable as commercial airplanes. This would help in bringing down the cost of spaceflight and boost its efficiency. The current industry practice in this case is tossing the multi-million dollar components after each launch. After some early crashes, SpaceX has now perfected the art of firing the booster's engines, maneuvering the grid fins and neatly landing the tall portion of the rockets upright on solid ground and on ocean platforms.
- Colonizing Mars: Elon Musk's dream is to make humans an "interplanetary species" by establishing a colony of people living on the Mars. Riding on reusable rockets and spaceships -- still under development -- people could travel 100 at a time to the Red Planet. The idea is to bring up to a million people to Mars in the next century. Test flights could start in the next decade. The cost to develop the rocket and spacecraft is estimated at $10 billion.
- BFR: SpaceX is calling the rocket that would carry all these people to Mars "BFR" or "Big Falcon Rocket." The idea is to have one booster and ship that replaces three of SpaceX's signature projects: the Falcon Heavy which aims to be the world's most powerful rocket for now, and may one day ferry supplies to Mars; the versatile Falcon 9 rocket, which can land seamlessly back on Earth post-launch and the Dragon cargo ship which supplies the International Space Station.
- Cargo and crew to space: SpaceX made history in 2010 by becoming the first private company to send its own spaceship to orbit and recover it. In 2012, SpaceX broke barriers again, sending its Dragon cargo ship to the orbiting International Space Station. That same year, SpaceX began regular cargo missions to supply the astronauts living in space with its gumdrop-shaped Dragon cargo ship, launched atop the Falcon 9 rocket, under a $1.6 billion contract with NASA.
Comments